lv systolic dysfunction grading | Assessing LV Systolic Function: From EF to Strain Analysis lv systolic dysfunction grading Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in relation to the volume of the blood in the ventricle at . FTB Interactions is the largest and most ambitious progression pack FTB has developed to date. The pack was designed to encourage cross-mod interactions to solve logistical challenges, defeat buffed mobs, outright cheese traditional obstacles, and even automate the killing of bosses.
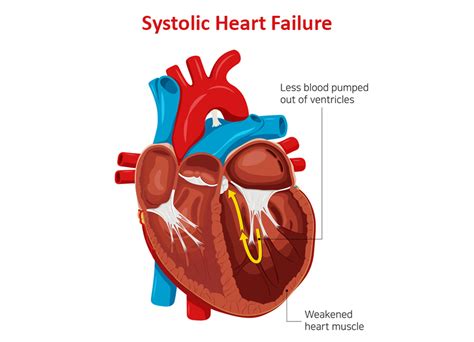
0 · Systolic Heart Failure: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
1 · Left ventricular ejection fraction (echocardiography)
2 · Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction
3 · Latest British Society of Echocardiography recommendations for
4 · LV function echocardiography • LITFL • CCC Cardiology
5 · Ejection Fraction Heart Failure Measurement
6 · Echocardiographic Assessment of Left Ventricular Systolic
7 · Echocardiographic Assessment of Left Ventricular
8 · Diagnosis and Management of Diastolic Dysfunction
9 · Classification of Heart Failure According to Ejection
10 · Assessing LV Systolic Function: From EF to Strain Analysis
Lady Gaga Brought Bradley Cooper Onstage for a Duet in Las Vegas Last Night | Vogue. Music. Lady Gaga Brought Bradley Cooper Onstage for a Duet in Las Vegas Last Night. By Christian.
There is growing evidence that patients with severe aortic stenosis and LVEF 50-60% have a higher rate of adverse outcomes compared to patients with LVEF >60%. A meta-analysis suggests that impaired LV GLS despite LVEF >50% is associated with reduced survival.Left ventricular systolic function can be assessed by quantifying the rate of change of the mitral regurgitant jet, with normal function showing a rapid . Diastolic heart failure occurs when signs and symptoms of heart failure are present but left ventricular systolic function is preserved (i.e., ejection fraction greater than 45 percent). The proposed nomenclature based on left ventricular ejection fraction defines “heart failure with reduced ejection fraction” (HFrEF) as LVEF .
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in relation to the volume of the blood in the ventricle at . phases of relaxation = isovolumetric relaxation, early filling, diastasis (when LA .
Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement that represents the percentage of blood the left . Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is a surrogate for left ventricular global .As addressed in the recent publication (1), the latest BSE guidance for LV function .
There is growing evidence that patients with severe aortic stenosis and LVEF 50-60% have a higher rate of adverse outcomes compared to patients with LVEF >60%. A meta-analysis suggests that impaired LV GLS despite LVEF >50% is associated with reduced survival. A normal heart’s ejection fraction is between 55 and 70 percent. This indication of how well your heart is pumping out blood can help to diagnose and track heart failure. It is important to note, however, that you can have a normal ejection fraction measurement and still have heart failure.
Left ventricular systolic function can be assessed by quantifying the rate of change of the mitral regurgitant jet, with normal function showing a rapid increase in LV pressure into the low-pressure left atrium. Diastolic heart failure occurs when signs and symptoms of heart failure are present but left ventricular systolic function is preserved (i.e., ejection fraction greater than 45 percent). The proposed nomenclature based on left ventricular ejection fraction defines “heart failure with reduced ejection fraction” (HFrEF) as LVEF of <40%, “heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction” (HFmrEF) as 40% ≤ LVEF < normal, and “heart failure with normal ejection fraction” (HFnEF) as LVEF of ≥55% in men and ≥60% .
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in relation to the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of diastole (end-diastolic volume). phases of relaxation = isovolumetric relaxation, early filling, diastasis (when LA passively fills LV and then stops), atrial contraction; diastolic dysfunction = disorder of LV filling where LV is unable to fill to a normal LVEDV without an increase in end-diastolic pressure.Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement that represents the percentage of blood the left ventricle pumps out with every contraction. It’s a sign of how well your heart is pumping blood. The normal, healthy range for EF measurement is 55% to 70%. An EF .
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is a surrogate for left ventricular global systolic function, defined as the left ventricular stroke volume divided by the end-diastolic .As addressed in the recent publication (1), the latest BSE guidance for LV function categorisation (‘severely impaired’, LVEF ≤35%; ‘impaired’, LVEF 36–49%; ‘borderline low’, LVEF 50–54%; and ‘normal’, LVEF ≥55%) is clearly out of keeping with current guideline documents from international echocardiographic societies (American Society of Echocar. There is growing evidence that patients with severe aortic stenosis and LVEF 50-60% have a higher rate of adverse outcomes compared to patients with LVEF >60%. A meta-analysis suggests that impaired LV GLS despite LVEF >50% is associated with reduced survival. A normal heart’s ejection fraction is between 55 and 70 percent. This indication of how well your heart is pumping out blood can help to diagnose and track heart failure. It is important to note, however, that you can have a normal ejection fraction measurement and still have heart failure.
Left ventricular systolic function can be assessed by quantifying the rate of change of the mitral regurgitant jet, with normal function showing a rapid increase in LV pressure into the low-pressure left atrium.
Diastolic heart failure occurs when signs and symptoms of heart failure are present but left ventricular systolic function is preserved (i.e., ejection fraction greater than 45 percent). The proposed nomenclature based on left ventricular ejection fraction defines “heart failure with reduced ejection fraction” (HFrEF) as LVEF of <40%, “heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction” (HFmrEF) as 40% ≤ LVEF < normal, and “heart failure with normal ejection fraction” (HFnEF) as LVEF of ≥55% in men and ≥60% .
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in relation to the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of diastole (end-diastolic volume). phases of relaxation = isovolumetric relaxation, early filling, diastasis (when LA passively fills LV and then stops), atrial contraction; diastolic dysfunction = disorder of LV filling where LV is unable to fill to a normal LVEDV without an increase in end-diastolic pressure.Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement that represents the percentage of blood the left ventricle pumps out with every contraction. It’s a sign of how well your heart is pumping blood. The normal, healthy range for EF measurement is 55% to 70%. An EF .
Systolic Heart Failure: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is a surrogate for left ventricular global systolic function, defined as the left ventricular stroke volume divided by the end-diastolic .
mercon lv atf transmission fluid
lv ban trello
Item Details. Item No.: 270585. SKU: FOA-SM3072-LV. Collection Name: Cornelia. Title: Furniture of America Cornelia Beige Loveseat. Details: Add a statement to your home with this fashion-forward sofa collection. A perfect example of fine taste and luxurious style with perfectly placed nailhead trim, multiple back pillows and sloped arms.
lv systolic dysfunction grading|Assessing LV Systolic Function: From EF to Strain Analysis

























